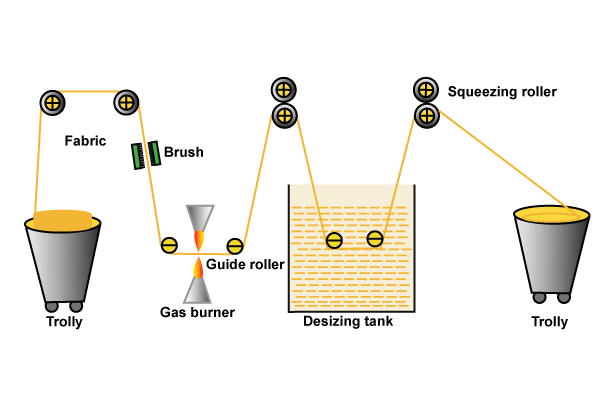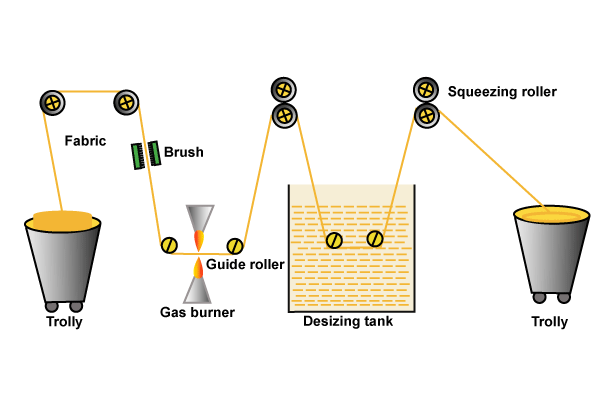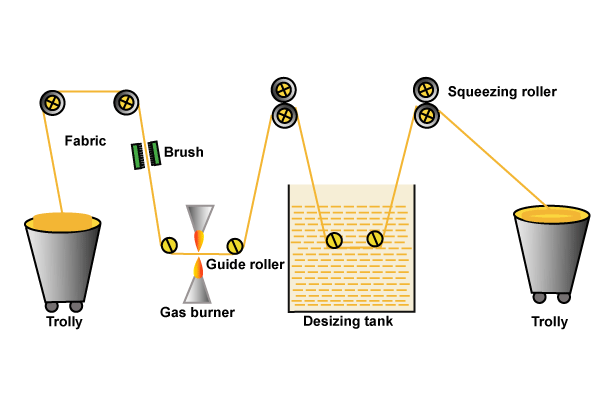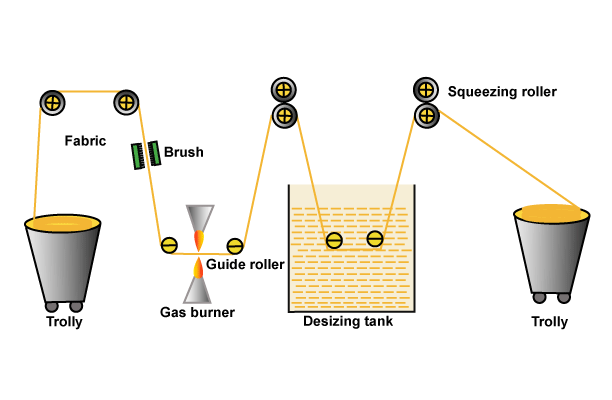
What is Pigment Printing | Advantages and Disadvantages of Pigment Printing
Definition of Pigment A substance in particulate from that is substantially insoluble in a medium but which can be mechanically dispersed in this medium to modify its color and light – scattering properties. In other ….. Read More