List of all the Natural Cellulose Fibres
Last updated on August 12th, 2023 at 11:38 pm
A fibre is obtained from a plant, animal, or mineral. Commercially important natural fibres are those cellulosic fibres obtained from the seed hairs, stems, and leaves of plants; protein fibres obtained from the hair, fur, or cocoons of animals; and the crystalline mineral asbestos. Vegetable fibres are generally comprised mainly of cellulose: examples include cotton, coir, kapok, jute, flax, ramie, hemp, pina, and abaca.

Seed Fibres
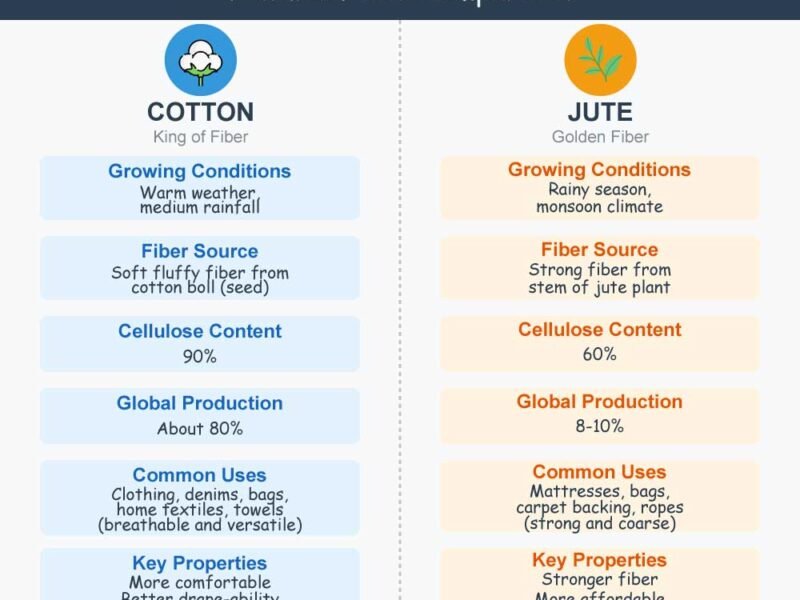
Cotton
Cotton is used to make several textile products. Cotton is a soft, staple fibre that grows in a form known as a boll around the seeds of the cotton plant, a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, including the Americas, India and Africa. The textile products include:
- Terry cloth is used to make highly absorbent bath towels and robes.
- The denim used to make blue jeans.
- Chambray, popularly used in the manufacture of blue work shirts (from which we get the term ‘blue-collar’).
- Socks, underwear, and most T-shirts are made from cotton.
- Bed sheets often are made from cotton.
- Cotton also is used to make yarn used in crochet and knitting.

Kapok
Kapok is a tropical tree. The word is also used for the fibre obtained from its seed pods. The tree is also known as the Java cotton, Java Kapok, or ceiba. The tree of life grows to 60-70m tall and has a very substantial trunk of 3m in diameter with buttresses. The box and many of the large branches are densely crowded with huge, robust, simple thorns. The leaves are compound of 5 to 9 leaflets, each up to 20 cm and plam like. Adult trees produce several hundred 15 cm seed pods. The pods contain seeds surrounded by a fluffy, yellowish fibre mixed with lignin and cellulose.

Bast Fibers
Flax
Flax is also known as linseed and is a member of the genus Linum in the family Linaceae. It is native to the region stretching from the eastern Mediterranean to India and was probably first tamed in the Fertile Crescent. This is called Jawas/Javas or Alashi in Marathi. Flax was extensively cultivated in ancient Egypt. New Zealand flax is not related to flax but was named after it as both plants produce fibres.

Ramie
It is a flowering plant. It is an herbaceous perennial growing to 1 – 2.5 m tall; the leaves are heart-shaped, 7 – 15 cm long, and 6 – 12 cm broad. And white on the underneath with tiny dense hairs gives it a silvery look; unlike nettles, the hairs do not string. The true ramie or China Grass, also called Chinese plant or white ramie, is the Chinese cultivated plant. A second type is known as green ramie or rhea and is believed to have originated in the Malay Peninsula.

Hemp
Hemp fibres are mainly used for ropes and aerofoils because of their high suppleness and resistance within the harsh environment. Hemp fibres are, for example, currently used as a seal within the heating and sanitary industries.

Hemp is used for various purposes, including the manufacture of cordage of varying tensile strength, clothing and nutritional products. The bast fibres can be used in 100% hemp products but are commonly blended with fibres such as flax, cotton or silk, apparel, and furnishings, most commonly at a 55% /45% hemp/cotton blend. The inner two fibres of hemp are woodier and are more often used in non-woven items and other industrial applications, such as mulch, animal bedding, and litter.
Jute
Jute fibre is obtained from the bark of Jute plants. This is the most well-known tropical fibre to meet the world’s demand for more affordable packing materials for various commodities. Some countries where jute cannot be cultivated have since been trying to grow a suitable replacement. As a result, ‘kenaf’ has been produced in certain parts of America as a jute replacement. Therefore, jute fibre remains unrivalled for the manufacture of cheaper Bags, sacks, packs, carpets, etc.

Leaf Fibers
Pina
Pina fibers are from the leaves of the pineapple plant. It is used to manufacture lightweight, sheer, stiff fabrics for apparel, bags, and table linens. It is also used to produce mats.

Abaca
Abaca is a member of the banana tree family. The fibers are coarse and very tall (up to 15 feet). It is a tough, durable, and flexible fiber used for ropes, floor mats, table linens, apparel, and wicker furniture.

You may also like: Cotton Vs Jute: Find the Key Differences



this article is nice………………..thanks
Thanks for your nice comment…
Can you write more about it? Your articles are always helpful to me. Thank you!
The articles you write help me a lot and I like the topic