An Overview of Azo Dyes
Last updated on August 18th, 2023 at 09:17 pm
Introduction
The dyes containing azo groups – N = N – are called Azoic Dye. These are not ready made dyes but are produced by reaction of two components – Diazocomponent or Base/Salt and coupling component (Napthol). Azoic dye also named as Napthol, Branthol, Magic and Ice color. Dye formation in fiber occurs on the basis of coupling reaction.
RN2Cl + Rʹ -ONa → R-N=N-Rʹ -OH

Normally two baths are needed for dyeing:
- Impregnation bath.
- Developing bath.
Properties/Significance of Azo Dyes
- These dye stuffs always contain Azo groups in its chemical structure.
- Light fastness property is admirable.
- Brightness of shade is also admirable.
- It is directly insoluble in water.
- These dye stuffs are always used in dyeing cellulosic material.
- Here dyeing operation is completed by two bath arrangement. One is called impregnation bath and another is called developing bath.
- Alkali resistance is poor to good. Index is 2 to 4.
- Suitable for lighter shade dyeing (Light resistance: Poor to very good, Index 2 – 7).
- This dye stuff is called developed dye due to formation of dye in fiber during dyeing process.
- Addition of salt increases the substantivity.
- Napthol dispersed in alcohol, T.R. oil.
Why Azo Dye is so called?
This color contains insoluble azo groups (– N=N –) in its chemical structure. That’s why this color is called Azo color.
Azo Color Called ‘Ice’ and ‘Magic’ Color
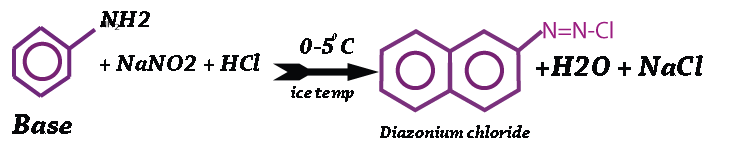
Ice Color
The coupling component is finally soluble in diazotization reaction. Diazotization is a chemical reaction where the base (Aromatic Amine) is to be converted to a solubilized form by the chemical reaction with NaNO2 at ice temperature (0 – 5˚C).
Magic Color
Two steps are required by dyeing with azoic color. In the first step textile goods are dyed by Naphthol color. In the 2nd bath, Base or Salt is used for dyeing. After 2 – 3 minutes dyeing in 2nd bath, the azoic color is seen in the textile goods magically. For this reason this dye is called Magic color.
Azo Dyes are Called ‘Naphthol’ and ‘Pigment’ Color
Naphthol Color
Azoic coupling components are insoluble in water. To make them soluble in water the textile materials are impregnated in a solution of Naphthol and NaOH. As the first coupling component is Naphthol color.
Pigment Color
Azoic dyes contain Azo group and final color is insoluble in water, so it is called Azoic Pigment.
Base (Soluble) + Napthol (Soluble) → Azoic dyes (Insoluble)
Procedure for Dyeing Cellulosic Material
Two bath of individual recipe is used for dyeing with azo dyes.
- Impregnation Bath.
- Developing Bath.
Impregnation Bath (1st bath)
Recipe:
Dye Stuff → 3% (According to the wt of the material)
NaOH → 2%
T.R. oil → 2%
Hot water → 3 times
Cold water → 7 times
HCHO → 1.5%
Temperature → 40˚C – 50˚C
Time → For a few minutes (2 – 3)
Developing Bath (2nd bath)
Recipe
Salt Bath
Fast salt → 6%
Hot water (30˚C – 40˚C) → 2 times
Cold water → 8 times
NaCl → 2% – 3%
Time → 2 – 3 minutes
Base Bath
Fast base → 3%
HCl → 2.5% – 3%
NaNO2 → 1.5%
Cold water → 10 times
Temperature → 0˚C – 5˚C
Time → 15 (2 – 3) minutes
Working Procedure
Dissolve NaOH in small quantity of hot water with Naphthol & T.R. oil in a bath and make a paste. Then add slowly in it, the rest hot water and stir (mix) constantly. After dissolving color perfectly and above mentioned cold water and finally the solution of Naphthol is thus obtained, this is cooled to 50˚C if necessary, HCHO may be added in the impregnated bath. Now the bath is ready for steeping textile goods for a few minutes (In this bath, any naphtholate goods, excepting the naphthol AS – G will look yellow).
In the developing bath salt is dissolved with hot water and then cold water added in the bath. Finally add NaCl in the developing bath. Now treating the above naphtholate or impregnated goods for 2 – 3 minutes in this bath. It will be noted that the color will develop the goods magically. Then squeeze the goods and boiling it in a soap bath followed by washing & drying. Now steep the textile goods for a while after developing a bath contains 1.5% of HCl in times of water. It is done only for neutralization of goods. Finally 3% soap and 1.5% soda is taken in a bath containing 15 times and treat the goods for a few minutes and wash the goods in fresh plain water. Then squeeze and dry. In this way, dyeing procedure is completed.
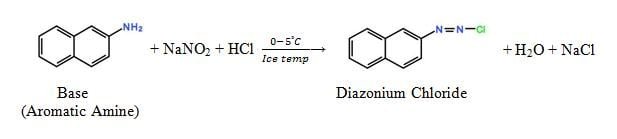
Diazotization
It is a chemical reaction where the fast base is to be converted to a solubilized form by the chemical reaction with NaNO2 at ice temperature (0 – 5˚C).
Function of Different Chemicals
Caustic Soda
- Soluble the dye material.
- Produce alkali medium.
T.R. oil
- Used as softening agent.
- Used as dispersing agent.
HCHO
- Ensure the actual level dyeing properties.
- For proper dyeing.
Salt
- To increase the substantivity of the azo color in textile materials.
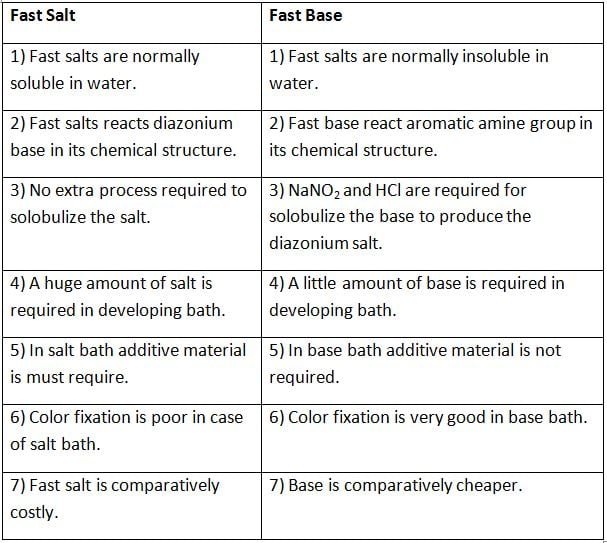
Difference Between Fast Salt and Fast Base
Stripping Method of Azoic Color
Stripping method of Azoic color:
Recipe:
NaOH → 4% (According to the wt of the material)
Na2S2O4 → 6%
Lissol Amine – A → 2% (Stripping promoter)
Water → 20 times
Time → 20–30 minutes
Temperature → Up to boiling (100˚C)
Azoic dye stuffs once developed are very difficult to strip. The yellow combination with AS – G and those with naphthol of high substantivity are the most difficult one to strip. In order to affect satisfactory stripping Lissol Amine – A is used. It acts as a stripping promoter, when used in conjunction with a reducing agent like sodium hydro-sulphide and alkali.
Method
The dyed material treated in a bath containing Lissol Amine – A, NaOH and sodium hydro – sulphide. 20 times of water of the dyed material is added. Now boil for 20 to 30 minutes until the shade is reduced to a pale (Light) yellow or brown color. The quantity of hydro – sulphide is increased in the case of yellow combination.
Precaution/Remarks in Dyeing with Azoic Dye
- Impregnation bath liquor can be preserved for a day or two days.
- Developing bath liquor cannot be preserved for a day.
- Naptholation material should never allow to come in contact with acid, alum and sunray.
- Generally 2 – 3 minutes duration is suitable for both impregnation and developing bath.
- If any way impregnating and developing liquor mixed together, the entire nature will be inactive and useless.
- During dyeing of protein fiber (Silk, Wool) with azoic dye, we should be very careful not to damage the protein fiber due to high alkali concentration.
- Bases yield comparatively better performance than salt.
Trade Name of Azoic Color

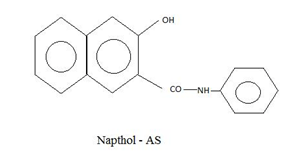
Chemical Structure of Azoic Dye
Test Method of Azoic Color
Take a sample dyed or printed with azoic color in a test tube in the presence of a reducing agent named Sodium Hydro/Bisulphide water liquor. Now treat the sample up to boiling stage. Then we will observe the color will come out completely from that sample. Now this liquor and sample are to come in an oxidizing action in the presence of air or an oxidizing agent. If the color is not received to it, then it will indicate that the sample are dyed or printed with azoic color.



Very important to know…
how to neutralize the used napthol and diazo salts for disposal after dyeing the cotton
I have collected your article by using Google search, thanks for your kind information
Informative and helpful article