Measurement of Yarn Hairiness
Last updated on August 24th, 2023 at 12:05 am
Definition of Yarn Hairiness
Spun yarns which are spun from staple fibres are hairy. It means that fibre ends come out of the main body of the yarn and its surface becomes hairy. It is a type of yarn fault. Sizing is done before looming the warp yarn to reduce its hairiness and after grey fabric is measured, sizing is done to remove hairy fibres from fabric surface.

Hairiness consists of protruding fibres, loop fibres, and loosely wrapped wild fibres.
Methods of Measurement of Yarn Hairiness
Several methods are available to measure yarn hairiness but three methods are very common in research laboratories. They are the following —
- Microscopic method.
- Singeing method.
- Photo electric principle.
List of Hairiness Testing Machine
- Shirley-Atlas hairiness tester.
- Zweigle hairiness tester.
- Meiners Dell hairinessw tester.
- Changling hairiness tester.
- Uster tester.
- Premier hairiness tester.
Effect of Yarn Hairiness
In spun yarn, hairiness is caused by the fibre protruding out of the yarn. The following are the effects of hairiness on yarn and fabric qualities —
- It imparts fuzzy appearance to the yarn and reduces luster of the yarn.
- It affects proper sizing of the yarn.
- It causes more yarn breakages during weaving due to the hairs in adjoining threads sticking together.
- It reduces fabric quality by creating weft bars in the fabric.
- It causes greater pilling in the case of polyester or cotton blended yarns.
Shirley Yarn Hairiness Tester
It is working on photo electric principle. Here optical technique is used to detect the fibre protruding from the body of the yarn.
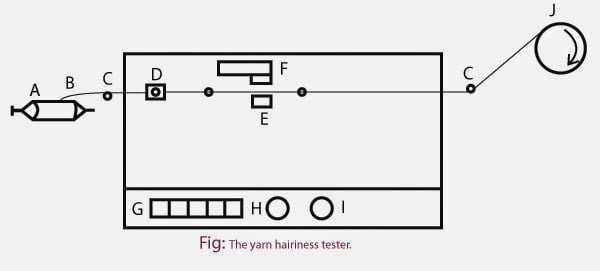
Name of the machine parts:
A = Yarn package,
B = Yarn,
C = Thread guides,
D = Tensioner,
E = Light source,
F = Photo-cell with hairiness adjuster,
G = Counter,
H = ON/OFF switch,
I = Yarn speed controller,
J = Yarn take up.
It consists of a photo-cell and a bulb from which a beam of light is made to fall on the photo-cell. The tester is provided with a tensioner by which a constant tension of 20 grams is given to the yarn and a thread guide which accurately locates the axis of the yarn relative to the beam of light and the photo-cell. The instrument can be set to measure the number of protruding fibres protruding by 3 mm and above. A five digit counter records the number of protruding fibres. The speed of yarn through the tester can be controlled between 60 and 120 yards per minute.
The yarn to be tested is passed through the tensioner and in between the photocell and lamp. As the yarn is drawn over the thread guide, the projecting fibres momentarily interrupt the light beam. The resulting signal from the photo-cell is amplified and if it then exceeds a certain threshold level, it is counted and displayed on the counter. The yarn so drawn is then wound on a winding drum whose speed can be varied between 60 and 120 yards per minute.



Hello. This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my previous room mate. He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this page to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing.
This actually answered my problem, thank you!