Inspection and Testing: Definition and Types
Last updated on September 24th, 2023 at 12:59 pm
Definition of Inspection and Testing
In order to maintain the required quality in the product it is necessary to have a well-defined quality control system to validate the quality of the various materials purchased and produced. Quality control is done through inspections and testing.
Inspection
Inspection is the process of visual identification of defects or non-conformity or other quality parameter which can be seen or identified by the eyes.
There are three types of inspection:
Raw Material Inspection
It is done for the raw materials which are used in the apparel production like fabric, sewing thread, button and other accessories etc. It is also termed as ‘incoming material inspection’. Normally this is done for fabrics using 4 point system or 10 point system.
Online or In-process Inspection
This is done during manufacturing process so that if there is any problem in the process that will be rectified in that stage itself. This will be carried out by the quality controllers periodically say every two or three hours. They will check the measurement and defects and make the inspection report which will be intimated to the production in-charge.
Final Inspection
This inspection is done after the goods are manufactured and packed in carton boxes and which are ready for the shipment. The goods are inspected and will be graded as per acceptable quality level (AQL) which is prescribed by the buyer. The goods can be shipped after the final inspection is passed.
Testing
There are certain quality parameters which cannot be visually measured or identified and those things can be measured or evaluated using certain instruments or equipment’s. This process is called as testing. For ex. Strength, shrinkage, flexibility, color fastness, weight etc. can be measured visually and requires some instruments to measure and evaluate these properties.
Normally the following tests are carried out in fabrics or garments as per the testing standards/procedures by the buyers:
- Fibre composition.
- GSM.
- Dimensional stability or Shrinkage.
- Flammability of textiles
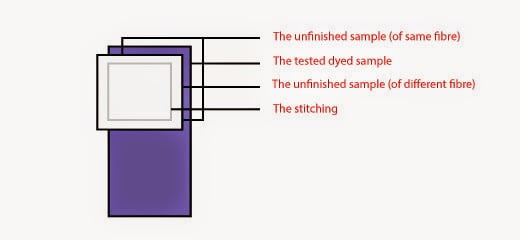
- Color fastness:
- Washing or Laundry
- Rubbing (Wet and dry)
- Light
- Perspiration or Saliva
- Pilling test
- Spirality/Bowing/Skewing
- Bursting
- Breaking strength
- Tearing Strength
- Azo test
- Ph and Formaldehyde
- Lead and Phthalate
- Fabric construction
If the fabric or garment is given any special finishing like water repellent, anti-bacterial or anti-microbial etc. then it should be tested for those testing also. The testing should be carried out in internationally recognized or buyer approved laboratory and the copies of testing reports should be sent to the buyer or buying office.
You may also like: What is Garment Sample? Types of Garment Sample



Thanks for the blog that covers a wide range of information on product inspection and testing.
Thanks for the share in inspection