What is carding? Definition and Meaning
Last updated on August 8th, 2023 at 12:00 am
Definition of Carding
Carding is the second stage of cotton spinning. It is defined as the reduction of entangled mass of fibres to filmy web by working them between two closely spaced relatively moving surfaces closed with sharp points i.e. wires.
The process of using a card (a thistle or teasel) for combing textile fibres. This consists of combing or brushing fibres until they are straightened and placed parallel. For this, the imperfect fibres and other impurities have to be removed. James Hargreaves and Louis Paul were two of the persons concerned with this invention and improvements to carding. Since then, innumerable attempts have been made to improve these machines, but in spite of this and also the latest improvements made, carding remains essentially the same as established nearly 200 years ago.
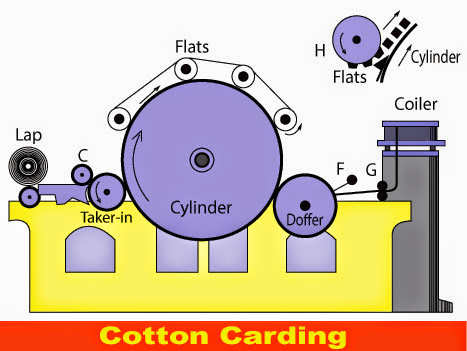
Cotton Carding
Since the functions of the card are to place the fibres parallel and remove other impurities so that perfect fibres can be drawn in sliver, the rollers of carding machine have to be so arranged, as would perform these functions perfectly.
Carding machine consists of 3 cylinders, covered with cards. (1) Taker-in is smallest, (2) Main cylinder is the largest and (3) The doffer. The outer contact cylinder lap feeds cotton to roller C, which rotates on a smooth iron table D. Here all the dirt is removed, and the fibres are straightened by combing. The cotton then passes along these cylinders as shown by arrows. The flats further flatten the fibres and also place them loose but parallel. When these are ultimately fed to doffer, its teeth draw these in light fleece and these are then further drawn into slivers, and deposited into coiler can G.
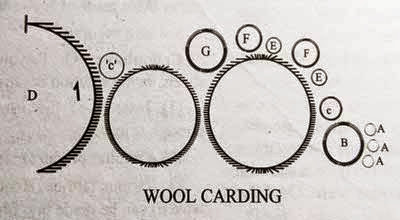
Wool Carding
Originally wool carding was done entirely by hand where two flat boards with teeth and convenient handles were employed for teasing out, lock by lock, and fibre by fibre, so that a perfect fibre-blending resulted.
In mechanical cards, this process becomes continuous by use of rollers, the arrangement of which is as shown in the above figure. Wool is carries forward with the machine on a travelling lattice and is fed to first feed rollers. This in turn is striped off by third, the forward-carrying-card-cylinder, and then passes over all the cylinders until completely carded wool passes out into slivers. These slivers are then wound on light bobbins and these bobbins are then placed on Mules for final roving and spinning operations.
You may also like: Objects and Tasks of Carding