Process Flowchart of Silk Production
Last updated on June 20th, 2023 at 07:35 pm
Silk is the very fine strand of fibre that is a solidified protein secretion produced by certain caterpillars to encase themselves in the form of cocoons. In spite of its high cost, it has been one of the most popular fabrics because of its unique characteristics. Soft, supple, strong and lighter in weight than any other natural fibre, it is prized for its lightness with warmth, sheerness with strength, and delicacy with resiliency. Actually, the whole commercial silk industry is based on one insect which is known as “silk worm”. When it wants to change in chrysalis, then a moth, the silk is made by it. It spins the silk filaments around itself in the form of a cocoon, inside which it can stay down in comfort.
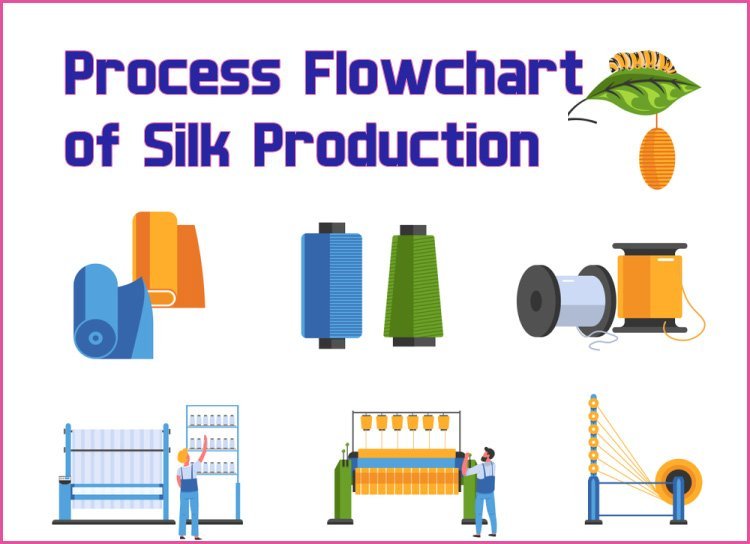
Flowchart of Silk Fibre Production
Cultivation of Silkworms
↓
Hatching
↓
Moulting
↓
Spinning the cocoon
↓
Sorting Cocoons
↓
Softening the Sericin
↓
Reeling the filament
Cultivation of Silkworms
The silk worm is the caterpillar of a small half moths belonging to “bombyx” which lives only on leaves of mulberry tree. The silk worm spent their entire life in eating these leaves.
Hatching
Eggs of silk worm are warm up for hatching in winter. It is done by spreading the eggs over the trays in the hatching shed and chopped leaves of mulberry trees are spread on the perforated paper. For eating the leaves, the worm climbs through the holes.
Moulting
After 35 days of hatching worm is 10000 times as heavy as it was born and it has become greenish white cater pillar. Now it is ready to start spinning, silk worm built its cocoon to settle down in it.
Spinning the Cocoon
The liquid silk comes from two glands called spinneret in the silkworm head, as the liquid comes out it is hardened into very fine filaments which are coated by a gummy substance called sericin which comes from other two glands nearly.
Sorting Cocoons
The cocoons are sorted according to color, size, shape, and texture, as all these affect the final quality of the silk.
Softening the Sericin
The cocoons are put through a series of hot and cold immersions, as the sericin must be softened to permit the unwinding the filament as one continuous filament.
Reeling the Filament
The process of unwinding the filament from cocoon is called reeling.



It is very useful to me for my assignment
Simply thanks!