Tappet, Dobby and Jacquard Shedding | Dwell Period | Advantages and Disadvantages of Tappet and Dobby Shedding
Last updated on September 22nd, 2023 at 10:05 pm
Tappet Shedding
By strongly beating the anti-friction bowl which is attached with cradle bowl in order to form shed for running arrangement of shuttle by the control of heald shaft is called tappet shedding. I.e. which types of shed are formed in tappet loom is called tappet shedding.

Dobby Shedding
The dobby is a shedding device placed on the top of a loom in order to produce a pattern by using a large number of healds than the capacity of a tappet. In fancy weaving the dobby is used to produce small pattern by means of warp threads and healds. The shed which is produced by a dobby is called dobby shedding.

Dobby is generally used to control 8-36 number of heald shaft for shedding.
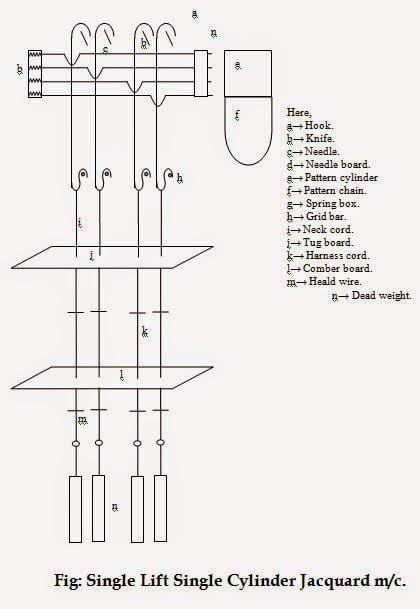
Jacquard Shedding
The jacquard is a shedding device placed on the top of the loom to produce large patterns by using a large number of warp threads separately by means of harness cords, hooks and needles. But no heald shaft is used here. The shed which is produced by jacquard is called jacquard shedding.

When more than 36 no. of warp required for shedding of a particular design, is done by jacquard shedding. It can be used to operate up to 2200 individual yarn for shedding.
Dwell Period
The tappet should be so made that headls will remain stationary while the shuttle passes through the shed. This stationary period is known as dwell of healds or dwell period or pause.
Or, Dwell is the stationary period when the heald frames do not change their position and shed remains open to allow the passage of the shuttle from one shuttle box to another.
The dwell period depend upon the following factors:
- The width of the fabrics. In narrow fabrics dwell will be short.
- In widths loom the dwell period will be long.
- In narrow R.S loom dwell period will be short and vice versa.
- For fine and tender warp dwell period will be short.
- For coarse, strong and elastic warp, dwell period will be long.
- If the picking force is high the dwell period will be short.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tappet Shedding
Advantages
- Simplest.
- Cheapest of all shedding motions.
- If conveniently employed, it gives the best result within its capacity.
- Action is certain.
- Less wear and tear.
- It can move healds at high speed.
- Dwell period may be adjusted to suit the type of fabric to be woven.
- Puts less strain upon the threads.
- Consumes less power and gives greater output.
- It causes fewer defects to the fabric.
Disadvantages
- Over shedding strains and breaks the warp threads.
- Under shedding does not permit the passage of the shuttle through the shed.
- Sometimes unequal shedding by lifting one end of the shaft more than other.
- Missed shedding.
- Unsuited dwell period.
- May impart jerky motion.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dobby Shedding
Advantages
- In this loom many numbers of healds can be used for weave a figured fabrics.
- Particularly 12-24 healds can be used in a cotton industry to weave fabrics.
- In which fabrics are not possible to weave in tappet shedding loom and jacquard loom for increasing the production cost, to weave this kind of fabrics dobby are used extensively.
Disadvantages
- Comparatively cost is high than tappet loom.
- Less productivity than tappet loom.
- Less speed.
- The adjustment of dwell is complicated.
- Maintenance cost is so high.
You may also like: Tappet Shedding: Definition, Types, Position and Construction