Premier Evenness Tester
Last updated on August 25th, 2023 at 10:28 pm
The task of a spinner is to transform a mass of millions of fibres with variable properties, tangled and containing unwanted foreign matter into a yarn characterized by uniformity of weight per unit length, diameter, TPI, colour, strength and so on. Now to test this uniformity different types of m/cs are used in textile technology. Evenness Tester is a machine that measures the evenness of yarn.
Theory
Evenness testing measures the uniformity of different yarn properties such as thick, thin places, neps, weights per unit length etc. The test also consists of the deviation of these property parameters from the average and their graphical presentation in the chart. A schematic diagram of the m/c is shown in the following figure. Two oscillators, A and B, have equal frequencies when there is no material in the measuring capacitor C. When the two frequencies have superimposed, the difference in frequency is zero. The presence of the material in the capacitor causes its capacity to change and alter the frequency of oscillator A. There will then be a difference between the two frequencies, which varies according to the amount of material between the capacitor plates.
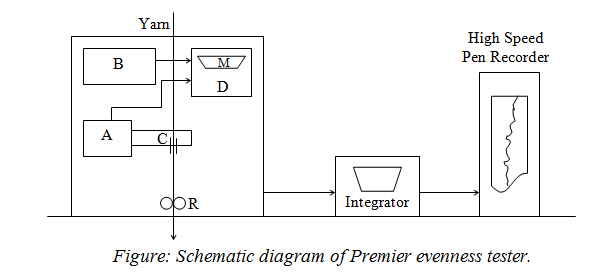
Suitable circuits D translate these frequency differences into signals which (1) are indicated on the meter M, (2) drive the pen of the recorder and (3) are fed into the integrator, which indicates the average irregularity either as percentage mean deviation or coefficient of variation. This is why another common name of this m/c is Electronic Capacitance Tester. The yarn speed for testing must be chosen so that the frequency of the fluctuations lies within the recording pen’s capacity to follow them. Again the chart contraction is to choose to suit the type of variation being examined. We should also select the capacitors to achieve a linear change in a capacity related to the plates’ amount of material. The thickness of the material relative to the size of the capacitor must not exceed certain limits.
Main parts
- 4 measuring capacitors
- Creel
- Guide
- Traverse rollers
- Meter
- Integrator
- High-speed pen recorder.
Functions
The m/c can do the following functions:
- It can measure the thick, thin places, neps etc.
- It can give graphical charts of the irregularities.
Limitations
The m/c has the following problems/limitations:
- The changes in capacity are linearly related to the weight of the material present. The material thickness should not exceed 40 percent of the distance between the plates of the capacitor.
- The capacitor’s length should be as short as possible so that the weight variations are measured over short distances.
- The shape of the cross-section of the tested strand affects the change in capacity.
- The moisture in the material affects the magnitude of the change in capacity, a higher moisture content giving a more significant power shift.
You may also like: Tearing Strength of Textile Fabrics



Crimp Tester to calculate the crimp in yarn affected by knitting or weaving by taking apart the yarn from a piece of given-length fabric, unbending it under given force and measuring its length, to determine actual yarn usage.