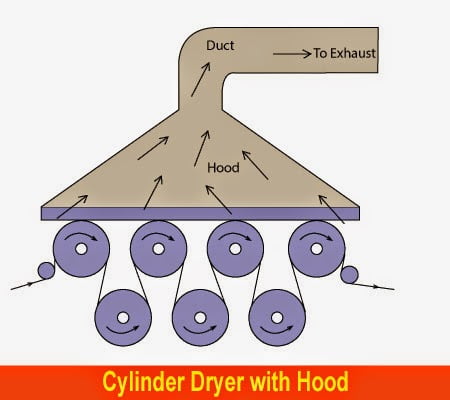
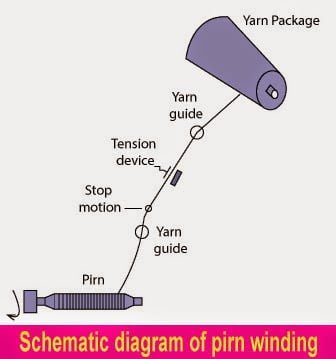
Properties of Textile Protein Fibre
Protein Fibre Properties Natural protein fibres are of animal origin. These are those fibres in which the fundamental chemical structure is composed of amino-acids joined in poly peptide chain. All protein fibres comprise the elements, ….. Read More